Auscot Gems: Unearthing Australia's Hidden Treasures
Explore the fascinating world of Australian gemstones and the stories behind them.
When Dinner Goes Wrong: The Sneaky Side of Food Poisoning
Discover the hidden dangers of dining out! Uncover shocking stories of food poisoning and how to keep your meals safe.
Top 5 Signs You Have Food Poisoning After Dinner
Experiencing discomfort after dinner can sometimes indicate that you've consumed contaminated food. One of the most common signs of food poisoning is nausea, which may start as soon as thirty minutes after eating. Other symptoms might include vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, these symptoms can vary based on the type of contaminant you ingested, so it's essential to pay attention to how your body reacts.
If you've eaten out, it's crucial to look for other signs of food poisoning such as fever and muscle aches. These symptoms can often be accompanied by a sense of fatigue and dehydration due to loss of fluids from vomiting and diarrhea. In severe cases, symptoms may worsen, leading to complications. For more detailed information on foodborne illnesses, you can visit FDA's food safety page for additional resources on prevention and treatment.
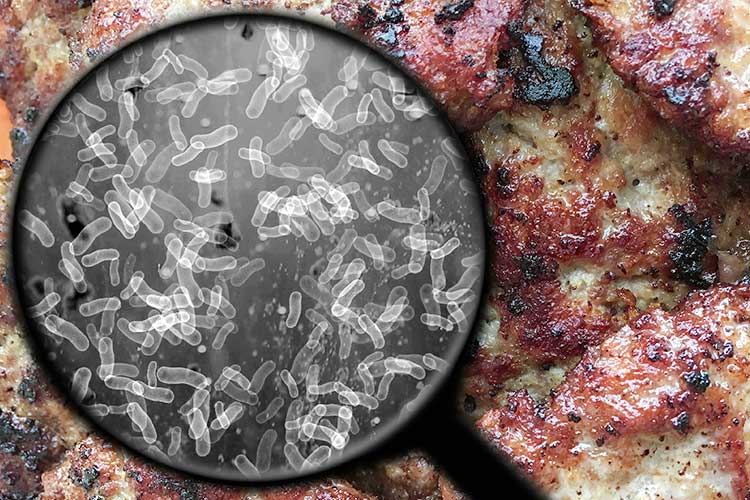
How to Identify Common Foodborne Pathogens
Identifying common foodborne pathogens is crucial for ensuring food safety and public health. These pathogens are mainly bacteria, viruses, and parasites that can contaminate food and cause illness. Some of the most common foodborne pathogens include Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria. To effectively identify these pathogens, it's important to be aware of their sources and symptoms they may cause. For instance, Salmonella is often found in raw poultry and eggs, while E. coli is typically linked to undercooked beef and contaminated produce.
To help in identifying these pathogens, organizations such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provide valuable resources. They recommend practicing safe food handling techniques, including thorough cooking, proper food storage, and avoiding cross-contamination. When symptoms of foodborne illness arise, such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea, it is vital to seek medical attention and report the incident to local health authorities. Understanding how to identify and mitigate risks associated with common foodborne pathogens is vital for maintaining public health and safety.
Is Your Dinner Safe? Tips to Prevent Food Poisoning
Ensuring that your dinner is safe starts with proper food handling practices. One of the key steps is to wash your hands frequently, especially before preparing food. According to the CDC, using soap and warm water for at least 20 seconds can significantly reduce the risk of spreading harmful bacteria. Additionally, make sure to wash all fruits and vegetables under running water and keep raw meats separate from other foods to avoid cross-contamination.
Temperature control is another critical factor in preventing food poisoning. Use a food thermometer to ensure that meats are cooked to their appropriate temperatures; for example, poultry should reach a minimum of 165°F to be safe for consumption. According to the USDA, perishable foods should not be left out at room temperature for more than two hours. By following these valuable tips, you can greatly reduce the risks and enjoy a safe dinner.